Describe the Orbitals Used by the Carbon Atom in Bonding
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. 10 Use the structure below to answer the following questions.
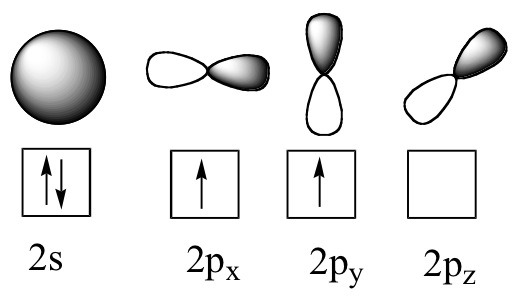
12 3 Hybridization Of Atomic Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts
A carbon atom that is sp3 hybridized can participate in a.

. Part B Describe the orbitals used by the carbon atom in bonding. H 2 CO d. How does Sulphur have vacant d-orbital.
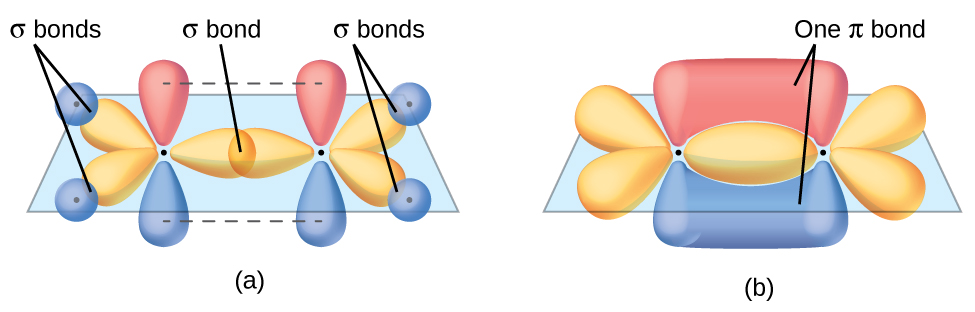
The remaining sp orbitals form σ bonds with hydrogen atoms. Transcribed image text. Science Chemistry Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Describe the orbitals used in bonding and the bond angles in the following compounds.
The number of hybrid orbitals formed is----- tothan the number of orbitals mixed and the ------ of hybrid orbital varies according to the specific orbitals mixed. These two perpendicular pairs of p orbitals form two pi bonds between the carbons resulting in. Part F Describe the orbitals used by each carbon atom in bonding and indicate the approximate bond angles.
Orbitals used for bonding that are formed by mixing atomic orbitals from the same atom. Select all that apply. How many π bonds are there between the carbon and the nitrogen.
Solution for Describe the orbitals used by each carbon atom in bonding and indicate the approximate bond angles1. How many σ bonds are there between the carbon and the nitrogen. The triple bond consists of one sigma bond and two pi bonds.
The Lewis structure is. Therefore the bond angles are 1095circ 4. The sp hybrid orbitals of the two carbon atoms overlap end to end to form a σ bond between the carbon atoms.
P two carbon to also has a speak to hybrid orbital because these are having a double bond arrest all carbon that is carbon number three 456 all have all the bones single so all of these carbon. And if one triple bond is made by a carbon atom then the orbitals involved are sp. Include all lone pairs of electrons.
Ethane C2H6 has 24 61 14 valence electrons. While if there is one double bond made by a carbon with other items then the hybrid orbitals involved are sP two. Each carbon atom still has two half-filled 2p y and 2p z orbitals which are perpendicular both to each other and to the line formed by the sigma bonds.
CH 3 O b. Bonds can be either one single one triple bond or two double bonds. A Lewis structure of H_2 C O_3 b the carbon uses s p2 hybridized orbitals.
90 10950 120 180 Submit Request Answer Part A CH33COH Draw the molecule by placing atoms on the canvas and connecting them with bonds. Orbitals used for bonding that are formed by mixing atomic orbitals from the same atom Hybrid orbitals are formed by the combination or mixing of -----orbitals from a specific atom. Because carbon forms a double bond we know that it uses s p2 orbitals as it does in ethene to bond to the two hydrogens and the oxygen.
Hence Sulphur has vacant d orbitals which can be used to expand the valency by the Sulphur atoms and form covalent bonds. The bond between carbon and single bonded oxygen atom is formed by hybrid orbital of carbon atom and hybrid orbital of oxygen atom. Which of the following statements correctly describe the bonding in the structure shown.
Because carbon is s p2 hybridized the bond angles are approximately 120circ. SOLUTION TO 31 b. Draw the molecule by placing atoms on the canvas and connecting them with bonds.
Therefore the bond angles are close to 120circ. Not all labels will be used. Chemistry questions and answers.
But oxygen doesnt have d orbitals thus cannot. Now if we assign Number two all the carbon atoms in this molecule then we will right. The hybrid orbitals of each carbon one by one carbon one has a double bond so its 100 orbitals R.
It uses its leftover p orbital to form the second bond to oxygen. A Use Valence-Bond Theory to explain the shape the angles and the hybridization of the central atom orbitals in the compound below. In this case the functional group is a carbocation.
According to MO theory one sigma orbital is lower in energy than either of the two isolated atomic 1s orbitals this lower sigma orbital is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. The two unhybridized p orbitals per carbon are positioned such that they overlap side by side and hence form two π bonds. What type of hybrid orbitals form around the carbon.
Because carbon forms a double bond we know that it uses s p2 orbitals as it does in ethene to bond to the two hydrogens and the oxygen. The pi bond between carbon and double bonded oxygen atom is formed by unhybridized p-orbitals of carbon and oxygen. Part E Describe the orbitals used by each carbon atom in bonding and indicate the approximate bond anges.
How many unmorphed p-orbitals remain on the carbon atom in this compound. The two π bonds of the triple bond are formed from parallel overlap of the two unhybridized p atomic orbitals from each carbon. Sp Draw the Lewis structure for H2CO3.
The six CH sigma bonds are formed from overlap of. Drag the appropriate them to their respective bins. One of the bonds is formed by side-on-side overlap of two sp2 orbitals.
Molecular orbitals for H2. The hydrogen atom attached to the alpha carbon atom is known as alpha hydrogen. The carbon atoms are sp3 hybridized.
Most Help 1100 HCN CCHCO. Describe the hybridization of the carbon atom in the hydrogen cyanide molecule H C N and make a rough sketch to show the hybrid orbitals it uses for bonding. Hybrid orbitals from each carbon atom.
B the carbon uses s p3 hybridizied orbitals. The two carbon atoms of acetylene are thus bound together by one σ bond. No on the basis of the fact that if all single bonds are made by a carbon then it utilizes its sP three hybrid orbital.
DONT DRAW ANY LOBES BUBBLES FOR THIS PART b Now draw those atomic orbitals you obtained in part a and then overlap them to form the C-F bonds you only have to draw ONE C-F bond and bonds of the CO. It uses its leftover p orbital to form the second bond to oxygen. When two atomic 1s orbitals combine in the formation of H2 the result is two sigma σ orbitals.
Sp3 None of the above Submit Request Answer Part C Indicate the approximate bond angles. CH 3 O b.
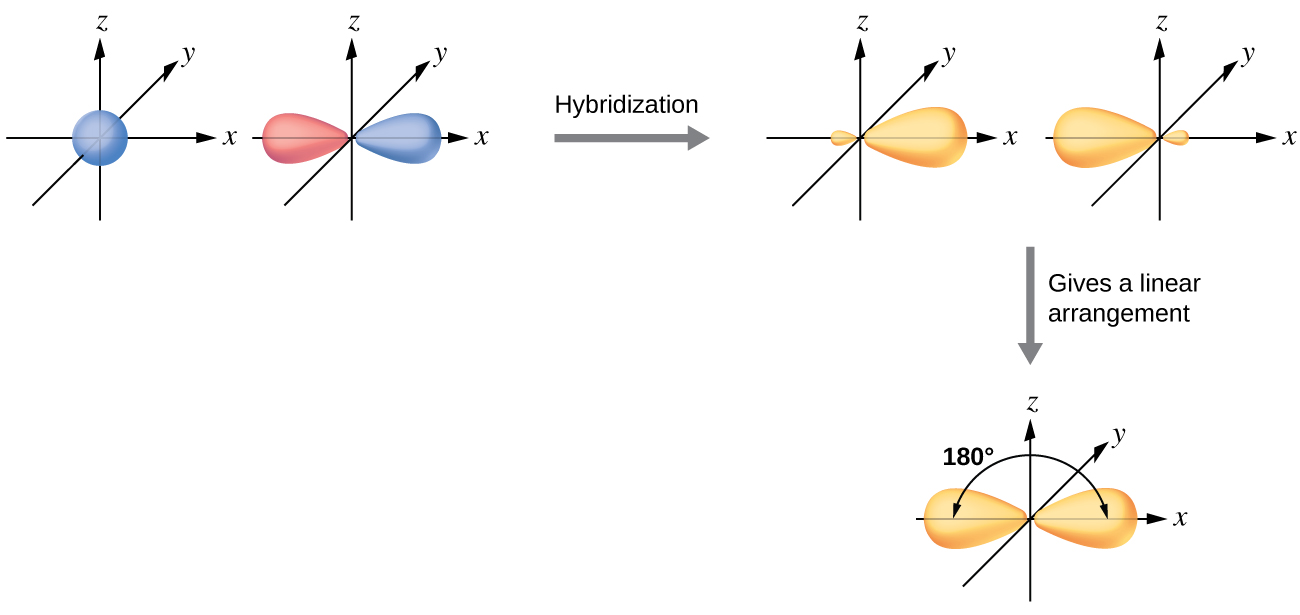
8 2 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals Chemistry

13 2 Molecular Orbitals For Ethene Organic Chemistry Ii

2 2 Hybrid Orbitals Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook

Lesson Explainer Hybridization Nagwa

Lesson Explainer Hybridization Nagwa
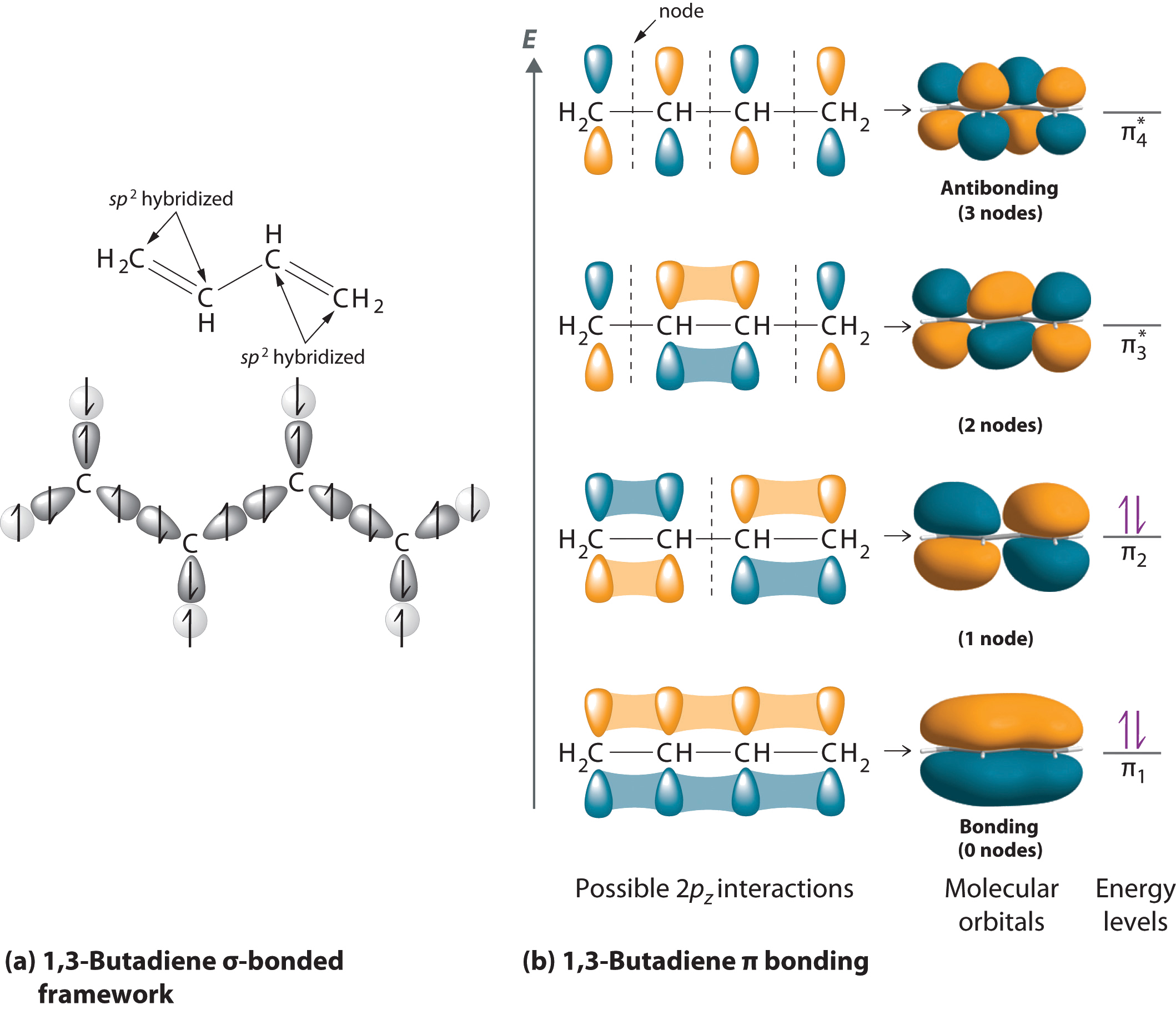
10 7 Multiple Bonding And Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts
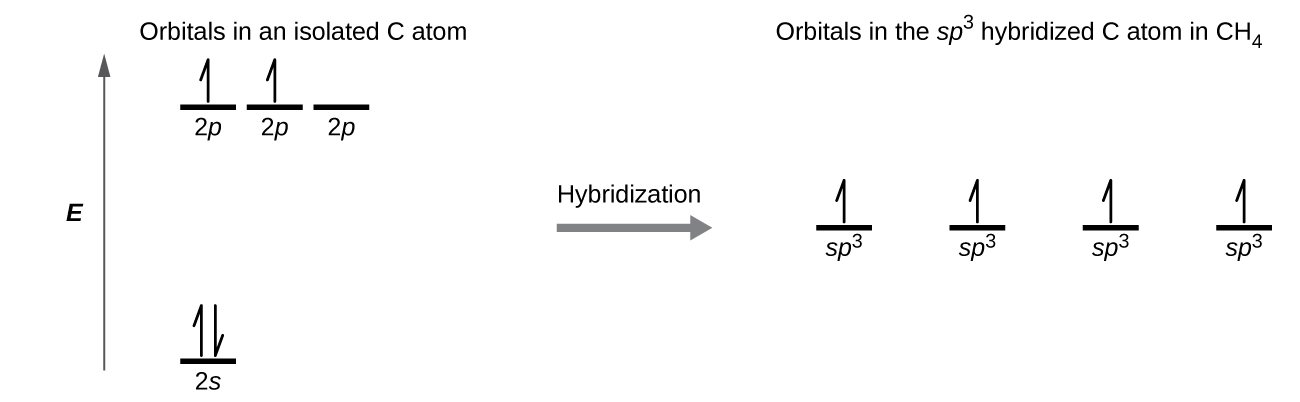
8 2 Hybrid Atomic Orbitals Chemistry

2 2 Hybrid Orbitals Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook

Hybridization Of Co2 Hybridization Of C O In Carbon Dioxide
1 Carbon Atom Orbitals From Left To Right S P X P Y P Z Orbitals Download Scientific Diagram

2 2 Hybrid Orbitals Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook

Lesson Explainer Hybridization Nagwa

Coordination Compound Ligand Field And Molecular Orbital Theories Britannica
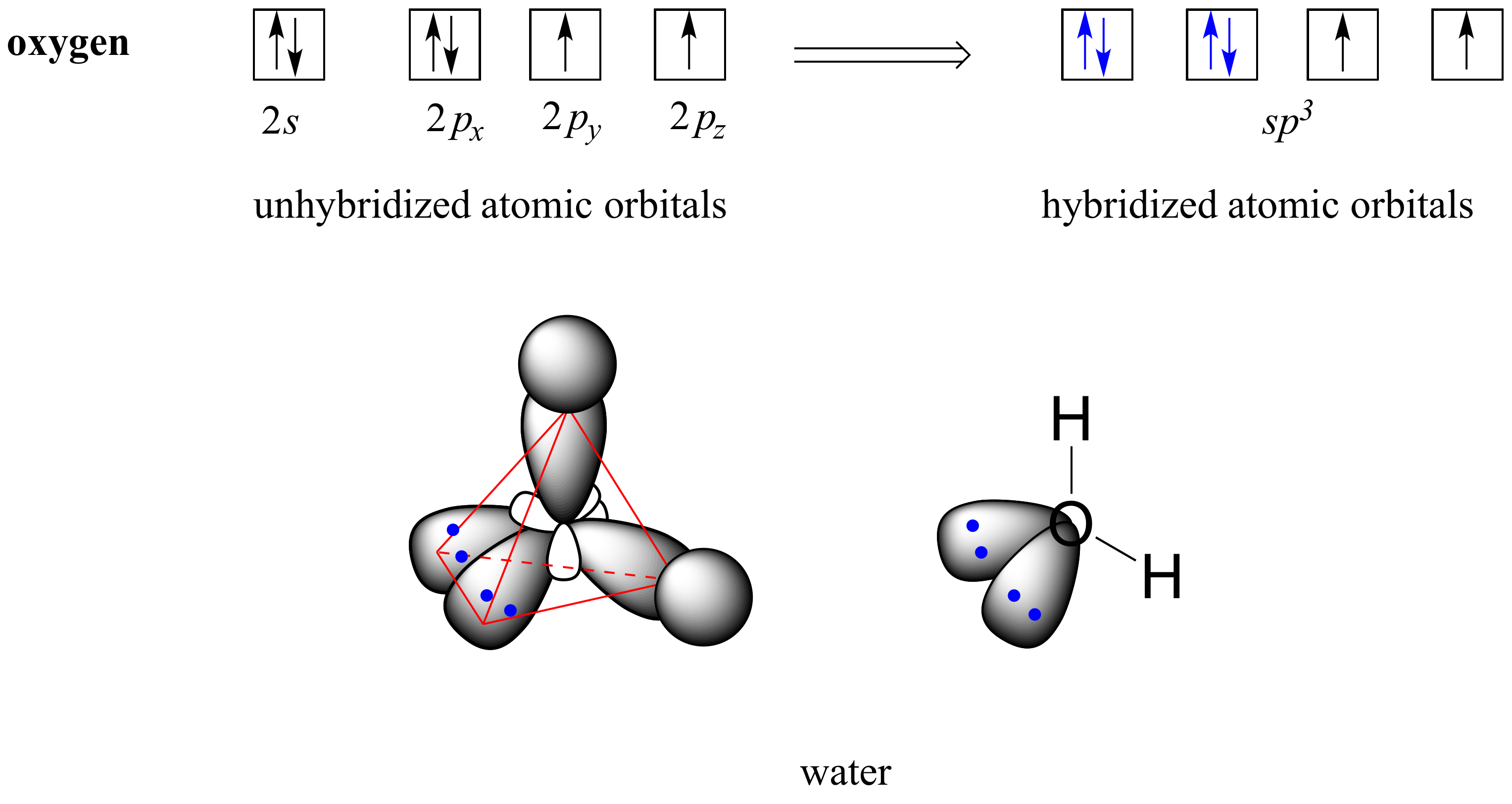
2 2 Hybrid Orbitals Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook
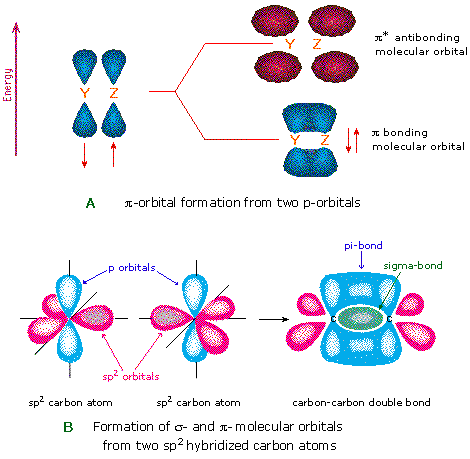
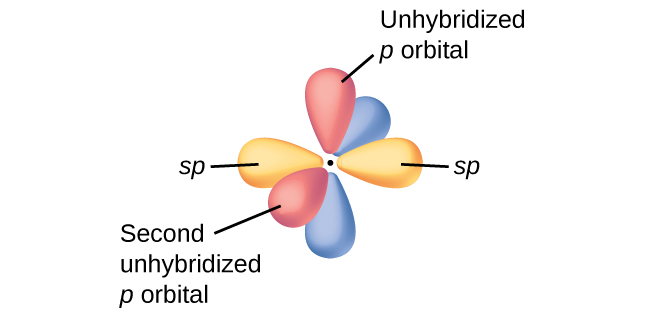
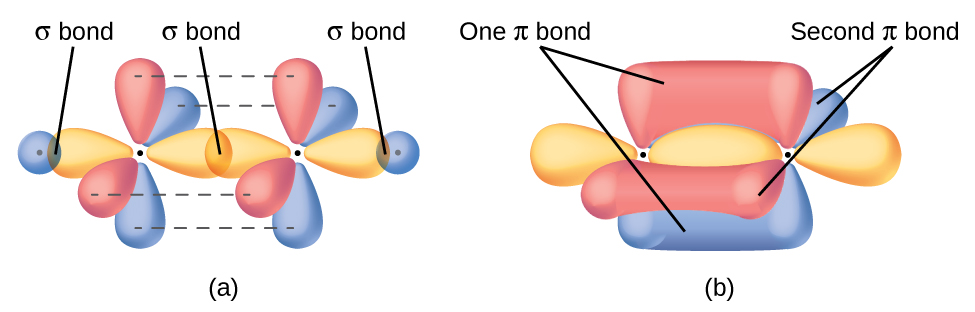
Comments
Post a Comment